The Father of Blood Banking
By Lisa Nails | Referral Specialist
Dr. Charles Richard Drew, an African American surgeon born in 1904, is known as the “Father of Blood Banking” for his significant contributions to the process of blood plasma preservation.
Dr. Drew attended medical school at McGill University in Montreal, Canada and became interested in blood transfusion during his residency. Later, he was awarded a Rockefeller fellowship at Columbia University where he wrote his thesis “Banked Blood: A Study in Blood Preservation” for his Doctorate in Medical Science. His research led to an appointment as the Medical Director of the Blood for Britain Project (BFB) during World War II, a program in which he implemented a uniform procedure for collecting and processing blood and plasma, successfully collecting over 14,000 blood donations.
Shortly after completing his work with the BFB, he was appointed assistant director of a national blood banking program in the US, sponsored by the American Red Cross where he developed one of his greatest innovations, mobile blood donation units. His work paved the way for the development of modern blood storage and transfusions.
Dr. Drew faced several racial barriers throughout his life, including being denied training and research opportunities. Most ironically, he was unable to donate blood to the very programs he helped establish at the American Red Cross due to their policies preventing Black people from donating blood. The policy was later modified but still required blood donations from Black and white people to be stored separately.
In response to the policies of the American Red Cross, he resigned from his position and began teaching at Howard University as the Head of the Department of Surgery while also serving as the Chief of Surgery at Freedmen’s Hospital. His mission was to train young African American surgeons to the highest standards. He was the first Black person to be appointed an examiner for the American Board of Surgery. Additionally, he continued to campaign against the exclusion of Black physicians from local and national medical organizations, including the American Medical Association.
Dr. Drew died tragically in a car accident at the age of 46. In his short lifetime, he broke through many racial barriers and made significant contributions to the fields of science and medicine.
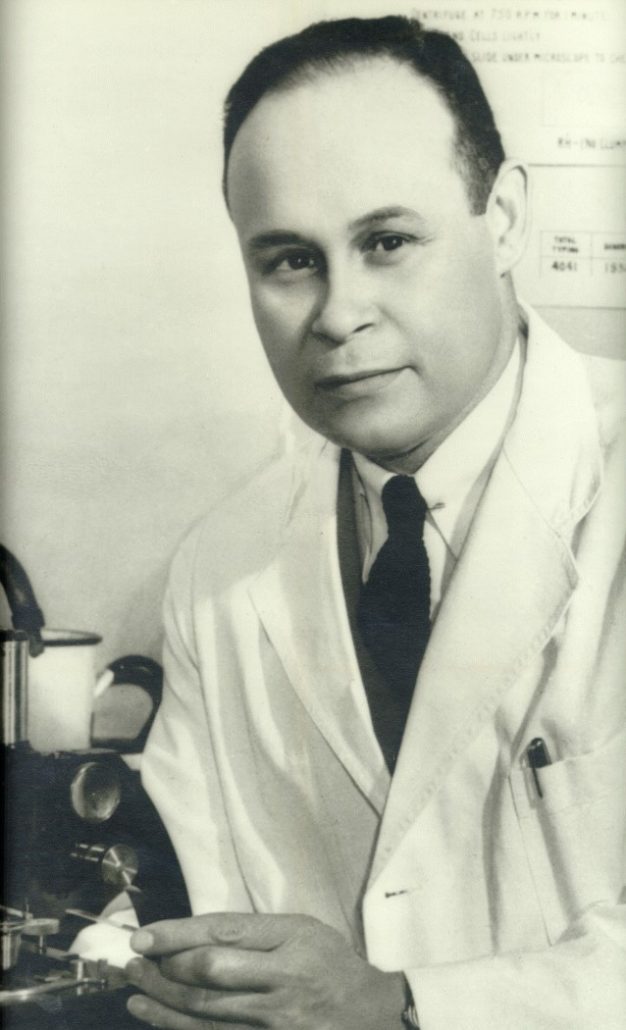

(1904-1950)